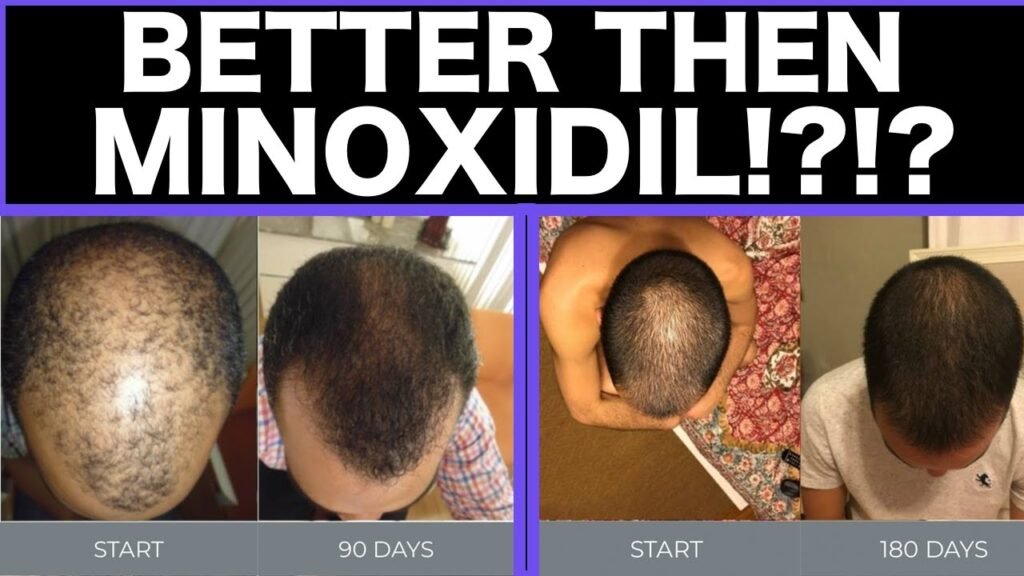
Side-by-side review of Minoxidil vs tretinoin
When considering treatments for hair loss and skin rejuvenation, both Minoxidil and tretinoin frequently emerge as popular options. Minoxidil, primarily recognized for its role in stimulating hair growth, is a topical solution applied directly to the scalp. It works by prolonging the anagen phase of hair follicles, thereby promoting increased hair density. On the other hand, tretinoin, a derivative of vitamin A, is well-known for its ability to enhance skin texture and treat acne, but it also has applications in promoting hair growth when used in conjunction with other treatments.
Effectiveness and Usage
Minoxidil is FDA-approved for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia and is available in concentrations of 2% and 5%. It is typically applied twice daily and is suitable for both men and women experiencing hair thinning. Conversely, tretinoin is often prescribed for its anti-aging properties and acne treatment, but studies have shown that it can enhance the efficacy of Minoxidil when used together. Tretinoin aids in increasing the absorption of Minoxidil into the scalp, thereby potentially improving results for hair regrowth.
Side Effects and Considerations
Both Minoxidil and tretinoin come with their own set of potential side effects. Minoxidil users may experience scalp irritation, dryness, or unwanted facial hair growth, particularly in women. Tretinoin, known for its skin-shedding properties, can lead to redness, peeling, and increased sensitivity to sunlight. When using these treatments, its crucial to follow the recommended application guidelines to minimize adverse effects. Additionally, while Minoxidil is often used alone, tretinoin is typically part of a broader skincare or hair care regimen, necessitating a more tailored approach to treatment.