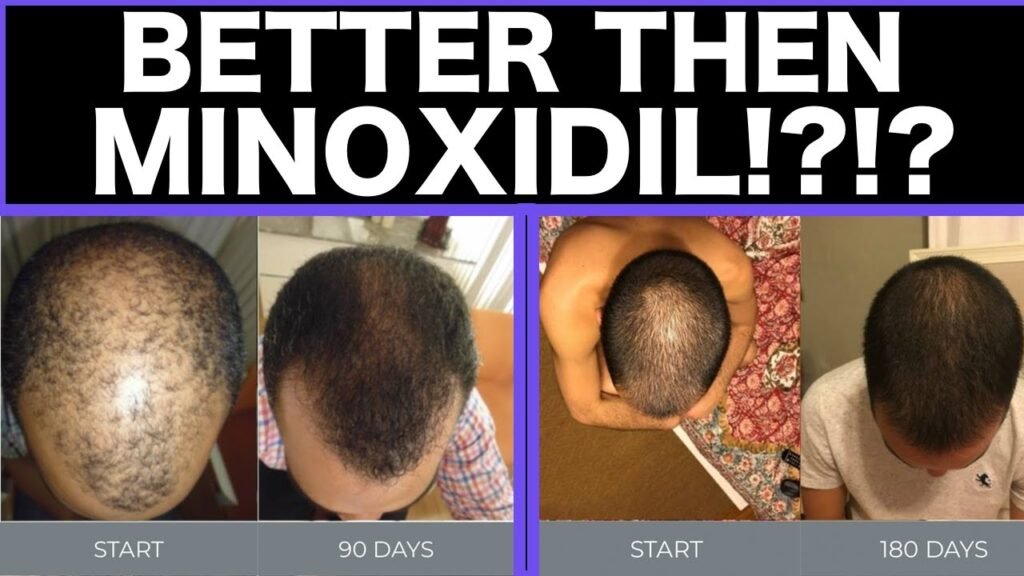
Minoxidil alternatives: Minoxidil vs finasteride
When considering alternatives to Minoxidil, Finasteride often emerges as a prominent option in the battle against hair loss. Both treatments are well-known in the dermatological community for their effectiveness, but they function through different mechanisms. Minoxidil is a topical treatment that works by stimulating hair follicles and increasing blood flow to the scalp, promoting hair growth and thickness. On the other hand, Finasteride is an oral medication that inhibits the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to hair loss.
Effectiveness and Usage
Minoxidil is typically applied directly to the scalp, making it a convenient option for those looking to target specific areas of thinning hair. Its often recommended for both men and women and is available over-the-counter in various concentrations. Users may notice results within a few months, but continuous use is necessary to maintain hair growth. In contrast, Finasteride is usually prescribed for men and is taken as a daily oral tablet. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to reduce DHT levels, thereby slowing hair loss and promoting regrowth. However, Finasteride is not typically recommended for women, especially those who are pregnant or may become pregnant, due to potential side effects.
Side Effects and Considerations
Both treatments come with their own set of potential side effects. Minoxidil users may experience scalp irritation or unwanted facial hair growth, while Finasteride users may face sexual side effects, such as decreased libido or erectile dysfunction. Its important for individuals to consult with a healthcare provider to determine which treatment aligns best with their health profile and lifestyle. Understanding the differences between Minoxidil and Finasteride, including their methods of application and potential side effects, can aid in making an informed decision about hair loss treatment.