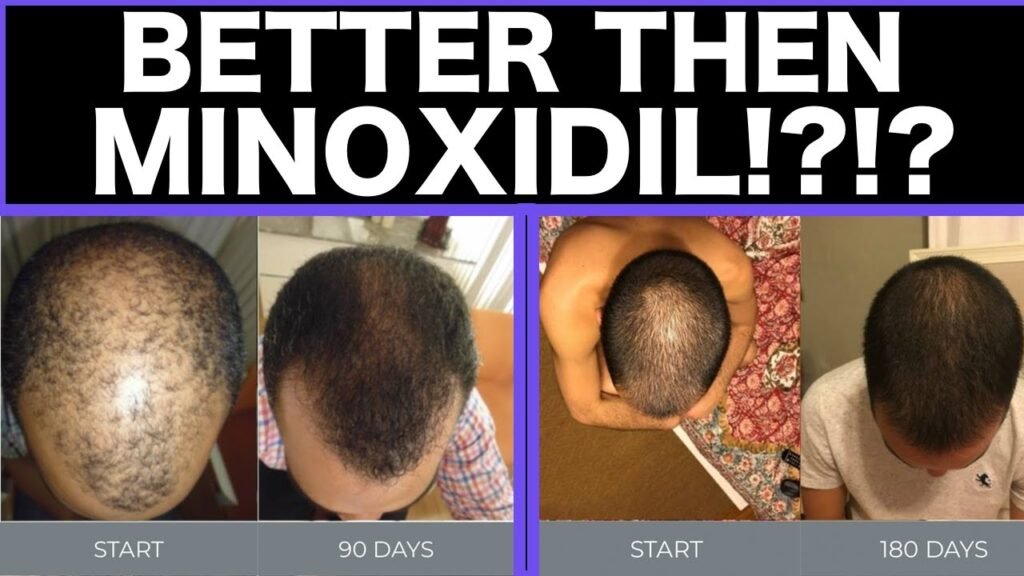
What works best: Minoxidil vs finasteride
When it comes to treating hair loss, two of the most popular options are Minoxidil and Finasteride. Both medications are FDA-approved and have shown significant results in promoting hair growth, but they work in different ways and are suitable for different types of hair loss. Understanding their mechanisms can help determine which might work best for you.
Minoxidil: The Topical Solution
Minoxidil is a topical treatment that is applied directly to the scalp. It works by stimulating hair follicles and increasing blood flow to the scalp, which can help to encourage hair growth. Minoxidil is most effective for individuals experiencing androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness. Users typically notice hair regrowth within three to six months of consistent use. However, its important to note that Minoxidil needs to be used continuously to maintain results, as stopping treatment can lead to a reversal of hair growth.
Finasteride: The Oral Medication
Finasteride, on the other hand, is an oral medication that works by inhibiting the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair loss. By reducing DHT levels, Finasteride can slow hair loss and, in some cases, even regrow hair. This treatment is often recommended for men with male pattern baldness and is usually taken in a 1mg daily dose. Unlike Minoxidil, Finasterides effects are systemic, meaning they affect the entire body, which can lead to more side effects such as decreased libido or erectile dysfunction in some users.
Both treatments have their pros and cons, and the choice between Minoxidil and Finasteride often depends on individual circumstances, including the type of hair loss, user preference, and tolerance for potential side effects. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance tailored to specific needs and conditions.