What’s the difference between Minoxidil vs tretinoin
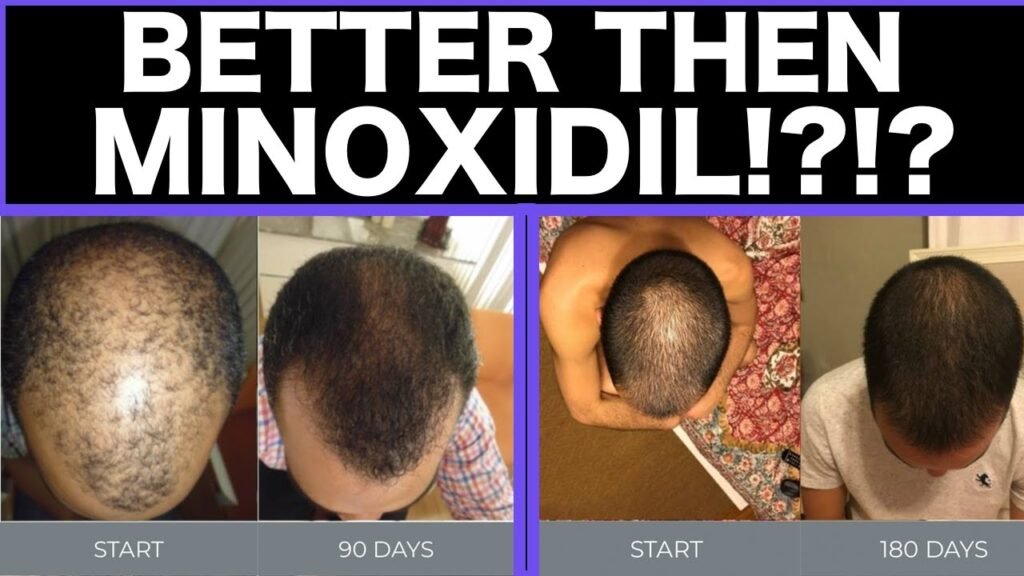
Minoxidil and tretinoin are both popular treatments in dermatology, but they serve distinct purposes and have different mechanisms of action. Minoxidil is primarily used as a topical treatment for hair loss. It works by stimulating hair follicles and increasing blood flow to the scalp, which can help to promote hair growth and prevent further hair thinning. Available in various concentrations, minoxidil is often applied directly to the scalp and is a common choice for those dealing with androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness.
On the other hand, tretinoin is a derivative of vitamin A and is commonly used to treat acne and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Tretinoin works by accelerating the skins cell turnover rate, helping to unclog pores and promote the shedding of old, damaged skin cells. This can lead to smoother skin and an improvement in skin texture. Unlike minoxidil, tretinoin is not typically used for hair growth but may be prescribed in combination with other treatments for certain skin conditions.
Application and Side Effects
The application methods for these two treatments also differ. Minoxidil is generally applied directly to the scalp, often twice daily, and can be found in both liquid and foam forms. Users may experience side effects such as scalp irritation or unwanted facial hair growth. Tretinoin, meanwhile, is typically applied to the skin once daily, usually in the form of a cream or gel. Common side effects include skin irritation, dryness, and increased sensitivity to sunlight, necessitating the use of sunscreen during treatment.
In summary, while both minoxidil and tretinoin are used in dermatological care, they target different issues and work through distinct mechanisms. Minoxidil focuses on stimulating hair growth, whereas tretinoin is aimed at improving skin health and appearance. Understanding these differences can help individuals choose the appropriate treatment for their specific needs.