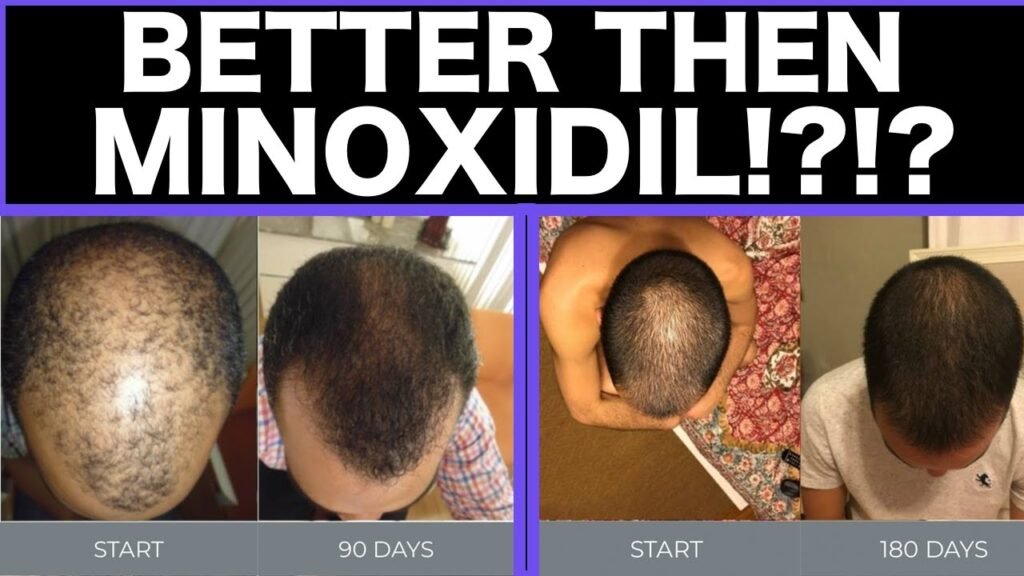
What works best: Oral minoxidil vs topical
When considering treatments for hair loss, the debate between oral minoxidil and topical minoxidil often arises. Both forms of minoxidil have proven efficacy in promoting hair growth, but their effectiveness can vary based on individual needs and circumstances. Understanding the differences in their application, absorption, and side effects can help individuals make informed decisions about which treatment may work best for them.
Effectiveness and Absorption
Topical minoxidil is widely known for its direct application to the scalp, where it is absorbed through the skin to stimulate hair follicles. This localized treatment can be effective for those experiencing hair thinning primarily on the scalp. In contrast, oral minoxidil is ingested and absorbed into the bloodstream, potentially offering a more systemic approach to hair regrowth. This systemic absorption may benefit individuals with more generalized hair thinning or those who do not respond well to topical applications.
Side Effects and Considerations
Each form of minoxidil comes with its own set of potential side effects. Topical minoxidil may cause scalp irritation, itching, or dryness in some users, which can be a drawback for those with sensitive skin. On the other hand, oral minoxidil may lead to more systemic side effects, such as changes in blood pressure or fluid retention, due to its absorption into the bloodstream. It is crucial for individuals to consult with healthcare professionals to weigh these side effects against the benefits, particularly if they have pre-existing health conditions.
Convenience and Compliance
The convenience of use can also influence the choice between oral and topical minoxidil. Topical minoxidil requires regular application, often twice daily, which can be time-consuming and may lead to inconsistent use if users find the routine cumbersome. Oral minoxidil, typically taken once daily, may offer a more convenient alternative for those seeking a simplified regimen. However, the choice between oral and topical forms should consider personal lifestyle, potential side effects, and overall treatment goals.